Memory in a computer is used to store data and instructions temporarily or permanently. It is mainly classified into Primary Memory and Secondary Memory.
1. Primary Memory (Volatile Memory)
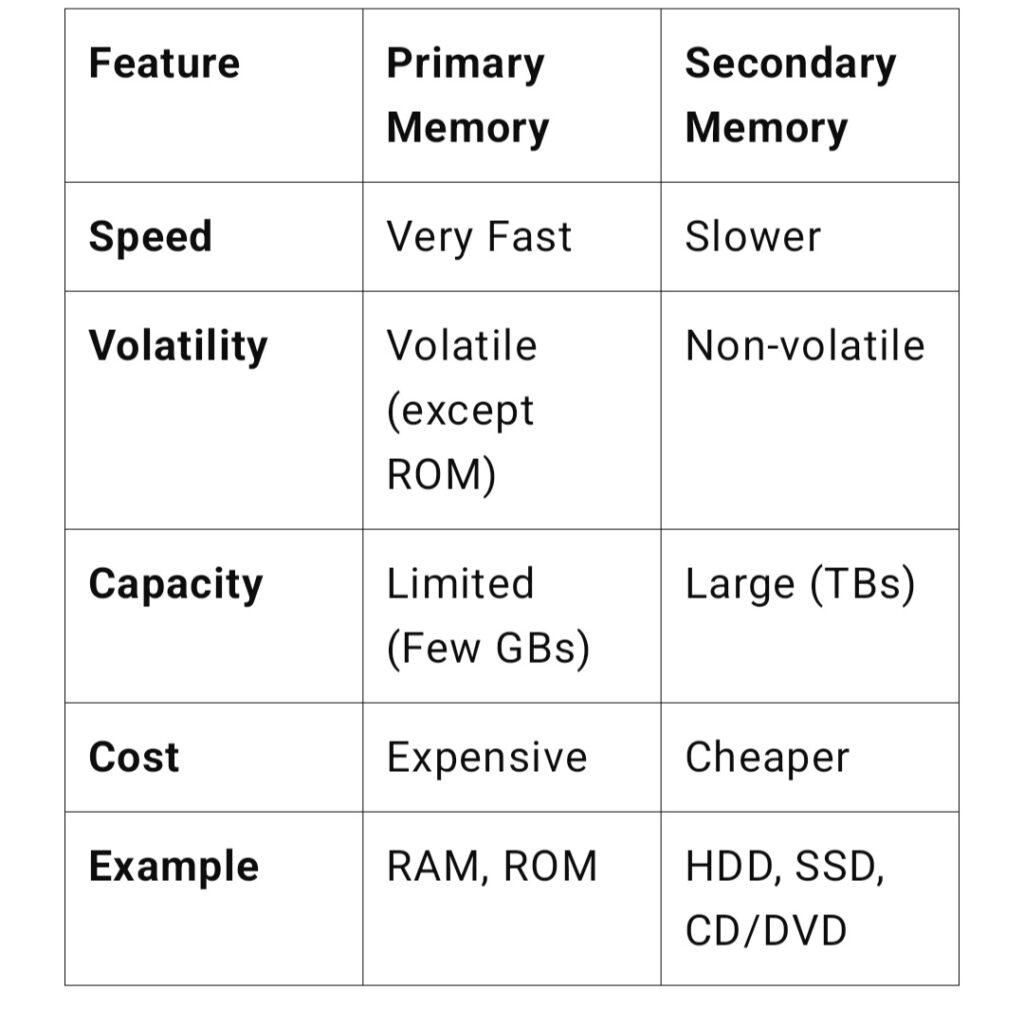
Primary memory is directly accessible by the CPU and is used for temporary data storage while the computer is running. It is faster but has limited storage capacity.
Types of Primary Memory:
- RAM (Random Access Memory) – Temporary memory used for running programs and processes.
- Types of RAM:
- SRAM (Static RAM) – Faster, used for cache memory.
- DRAM (Dynamic RAM) – Slower but cheaper, used as main memory.
- Types of RAM:
- ROM (Read-Only Memory) – Permanent memory storing essential instructions (like boot-up firmware).
- Types of ROM:
- PROM (Programmable ROM) – Can be written once.
- EPROM (Erasable PROM) – Can be erased using UV light.
- EEPROM (Electrically Erasable PROM) – Can be erased electrically, used in BIOS.
- Types of ROM:
Use of Primary Memory:
- Stores data temporarily for quick access.
- Holds active processes and running applications.
- ROM helps in booting up the system.
Watch Input-Output Devices PYQS
2. Secondary Memory (Non-Volatile Memory)
Secondary memory is used for long-term storage and retains data even when the computer is turned off. It is slower but larger in capacity compared to primary memory.
Types of Secondary Memory:
Secondary memory is non-volatile storage, meaning it retains data even when the computer is turned off. It is used for long-term data storage and has a much larger capacity compared to primary memory.
1. Magnetic Storage
Uses magnetized surfaces to store data.
- Hard Disk Drive (HDD) – Main storage device in most computers; stores OS, software, and files.
- Floppy Disk (obsolete) – Small, portable storage used in older computers.
- Magnetic Tape – Used for data backup in servers and archives.
2. Optical Storage
Uses laser technology to read/write data.
- CD (Compact Disc, 700 MB) – Used for audio, software, and small data storage.
- DVD (Digital Versatile Disc, 4.7 GB – 8.5 GB) – Stores videos, games, and software.
- Blu-ray Disc (25 GB – 128 GB) – Used for high-definition movies and games.
Watch Active-Passive Voice for sci cbse ssc
Join Supreme Court SCI_JCA Telegram Group
3. Flash Storage (Solid-State Storage)
Uses electronic memory (faster and more durable).
- Solid State Drive (SSD) – Faster alternative to HDD, used in modern computers.
- USB Flash Drive (Pen Drive) – Portable storage device for data transfer.
- Memory Card (SD Card, microSD) – Used in cameras, mobile phones, and tablets.
4. Cloud Storage
Stores data on remote servers, accessible via the internet.
- Google Drive, OneDrive, Dropbox – Cloud-based storage for files and backups.
- iCloud, Amazon S3 – Secure cloud storage for personal and business use.
5. Hybrid Storage
Combines different types of storage for better performance.
- SSHD (Solid State Hybrid Drive) – Mix of HDD and SSD, offering high speed and large storage.
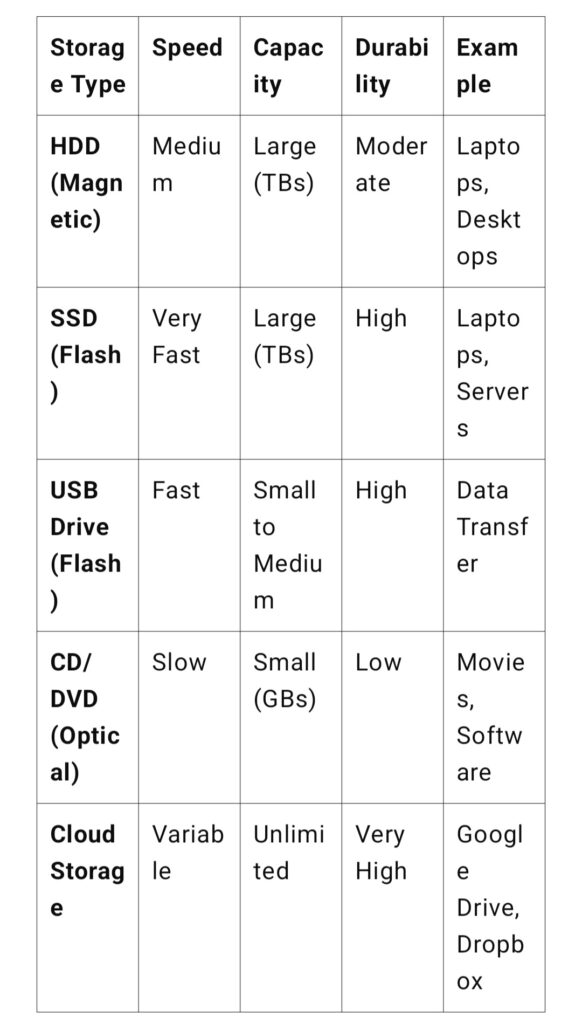
Comparison Table: Secondary Memory Storage Types
presentaffairs.in
Use of Secondary Memory:
- Stores files, software, and OS permanently.
- Used for backup and large data storage.
- Portable storage devices allow data transfer.
Comparison Table: Primary vs. Secondary Memory